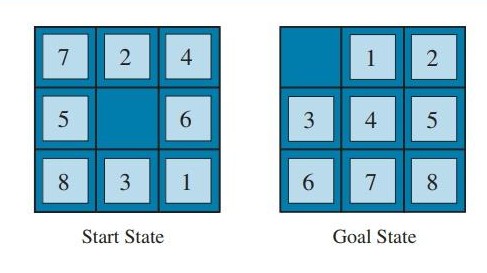
路径寻找-八数码问题
Hash与BFS

Hash与BFS
题目:洛谷·UVa 12166 题意 给一个深度不超过16的二叉树,代表一个天平。每根杆都悬挂在中央,每个秤砣的重量已知。至少修改多少个秤砣的重量才能让天平平衡?——刘汝佳《算法竞赛入门基础》 分析 乍一看似乎无从下手,我们可以先来研究一下平衡的天平具有什么性质 把每一个子天平都看作一个秤砣,若天平平衡,则其总重量等于其中一个秤砣的重量乘以2 设天平的深度为$ depth $。通过下图我们发现: $ 天平的总重量 = 任意一个秤砣的重量(包括把子天平看作秤砣) \times 2^{depth} $ 于是只要读入天平,记录 $ num \times 2^{depth} $ (num为秤砣的重量)重复的次数,结果为: $ 最少修改数 = 结点总数 - max(num \times 2^{depth}重复的次数) $ 利用STL的map映射可以很方便地解决本题 代码 #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); #define LL long long #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <cctype> #include <map> using namespace std; map<LL, int> cnt; // map映射:记录num*2**depth重复的次数 int solve(string s) { int depth = 0, sum = 0, maxn = 0; // 二叉树深度,结点总数,不需更改的结点数 int len = s.length(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (s[i] == '[') depth++; if (s[i] == ']') depth--; if (isdigit(s[i])) { LL num = 0; for (; isdigit(s[i]); i++) { num *= 10; num += s[i] - '0'; } // 字符转整数 i--; // 防止for循环导致的差1错误 sum++; cnt[num << depth]++; // cnt[num*2**depth]++ maxn = max(maxn, cnt[num << depth]); } } return sum - maxn; } int main() { #ifdef LOCAL freopen("uva12166.in", "r", stdin); freopen("uva12166.out", "w", stdout); #endif IOS int t; string s; cin >> t; while (t--) { cnt.clear(); cin >> s; cout << solve(s) << endl; } return 0; } C++ STL的map跟Python的字典很像,但也有区别:map能引用未赋值的键值对,且其值默认为0;而Python不能引用未定义的键值对 ...
题目:洛谷·UVa439 题意 输入一个m*n矩阵表示地图,其中1表示障碍,0表示空地。机器人要从m*n地图的(1,1)走到(m,n),每次可以往上下左右的其中一个方向走一格,且最多只能连续跨过k个障碍。数据满足1 <= m, n <= 20, 0 <= k <= 20 分析 首先我们可以确认这不是普通的BFS求最短路(对比:Uva 439),但题目多了一个条件——最多能连续跨过k个障碍,这意味着只用二位数组不足以判断题目条件 于是我试着用访问数组int vis[maxn][maxn][2]存储访问状态,其中vis[x][y][0]表示从该格再走一步后的步数,vis[x][y][1]表示走到该格需要跨越的障碍数。但这种思路存在问题:程序无法区分跨越不同数量的障碍走到同一格,而是把它们视为同一条路线 只需稍加改进,用bool vis[maxn][maxn][maxn]存储访问状态即可,其中vis[x][y][cnt]表示连续跨越cnt个障碍后到达(x,y) 利用结构体存储坐标、步数和连续跨越障碍的数量,方便BFS的入队出队操作(因为只需一个队列) 代码 C++ #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int maxn = 25; int pic[maxn][maxn]; // 读入地图 bool vis[maxn][maxn][maxn]; // 访问数组,判断是否曾连续跨过若干个障碍到达某格 const int dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; // 偏移量 const int dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0}; int t, m, n, k; struct Node { int x; int y; int step; // 当前步数 int cnt; // 当前连续跨越障碍的数量 }; void read_lines() { cin >> m >> n >> k; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) cin >> pic[i][j]; } bool check(int x, int y) { // 检查是否出界 if (x < 1 || y < 1 || x > m || y > n) return true; return false; } int bfs(int x, int y, int k) { Node t = {x, y, 0, 0}; queue<Node> q; q.push(t); while (!q.empty()) { t = q.front(); if (t.x == m && t.y == n) return t.step; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int px = t.x + dx[i], py = t.y + dy[i]; if (check(px, py)) continue; // 出界 Node tmp = {px, py, t.step, t.cnt}; // 一定要用临时变量来操作! if (pic[px][py]) tmp.cnt++; // 该格为障碍 else tmp.cnt = 0; // 该格为空地 if (tmp.cnt <= k && !vis[px][py][tmp.cnt]) { // 连续跨越障碍数量<=k且未曾连续跨过t.cnt个障碍到达(px,py) tmp.step++; vis[px][py][tmp.cnt] = true; // 已访问 q.push(tmp); } } q.pop(); } return -1; } int main() { #ifdef LOCAL freopen("patrol_robot.in", "r", stdin); freopen("patrol_robot.out", "w", stdout); #endif ios::sync_with_stdio(false); //取消cin与stdin的同步,加速输入输出 cin.tie(0); // 解除cin与cout的绑定,进一步加快执行效率 cout.tie(0); cin >> t; while (t--) { memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis)); // 记得清零! read_lines(); cout << bfs(1, 1, k) << "\n"; } return 0; } 我们知道cin和cout输入输出的速度比不上printf和scanf,因此可以通过一些小技巧来加速: ...

第一次写题解惹~ 简单,但是卡了好一会,最后发现是忘了清零数组 XD 题目:洛谷·UVa439 题意 输入8*8国际象棋棋盘的两个坐标(起点和终点。列:ah,行:18),求出马(Knight)从起点到终点所需最少步数 分析 典型的BFS求最短路问题。二维数组id[10][10]存储从该格再走一步后的步数,队列qx,qy存储坐标 注意到每个格子不能重复,否则无法算出最短路 代码 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <queue> #include <cstring> using namespace std; // 偏移量:马能走的八个方向 const int dx[8] = {-1,-2,-2,-1,1,2,2,1}; const int dy[8] = {2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1,1,2}; int id[10][10]; int bfs(int x, int y, int x_target, int y_target) { if (x == x_target && y == y_target) return 0; // 起点即终点 queue<int> qx, qy; qx.push(x), qy.push(y); id[x][y] = 1; while (1) { x = qx.front(), y = qy.front(); for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newx = x + dx[i], newy = y + dy[i]; if (newx == x_target && newy == y_target) return id[x][y]; if (newx < 1 || newy < 1 || newx > 8 || newy > 8 || id[newx][newy]) // 出界或已走过的点 continue; qx.push(newx), qy.push(newy); id[newx][newy] = id[x][y] + 1; } qx.pop(), qy.pop(); } } int main() { #ifdef LOCAL freopen("knight_moves.in", "r", stdin); freopen("knight_moves.out", "w", stdout); #endif string start, target; while (cin >> start >> target && start.length() && target.length()) { memset(id, 0, sizeof(id)); // 记得清零! cout<<"To get from "<<start<<" to "<<target<<" takes "; cout<<bfs(start[1]-'0', start[0]-'a'+1, target[1]-'0', target[0]-'a'+1)<<" knight moves.\n"; } } P.S.小技巧 你应该注意到了,我采用了重定向输入输出,却没有在代码里定义LOCAL符号——其实我已经在编译选项里编译了 这样做的好处是,在本地调试时默认为重定向输入输出,提交到oj时自动忽略编译重定向这段代码,方便且能避免出错 只需在编译时加上-DLOCAL这条参数即可。我的做法是修改Sublime Text的编译系统文件: ...

减少不必要的枚举
最近看什么都像二叉树(
简单而又不简单