题目
玩过华容道吧?或者是Win7自带小挂件的数字滑块游戏?八数码问题就是从这个游戏引申出来的:
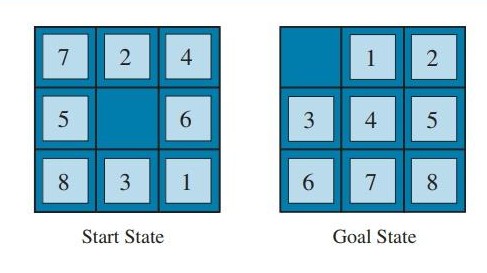
给定编号为1~8的正方形滑块,排成 $ 3 \times 3 $ ,其中有一个格子留空。每次操作可以把一个与空格相邻滑块移动到空格内。给定初始局面和目标局面(空格用0表示),求最少移动步数,若无法到达目标局面,则输出
-1
分析
可以看出,这也是BFS求最短路。但要注意判重,即避免同一个访问多次,否则会相当浪费时间和空间
对于本题, 哈希(Hash) 是一种可行而高效的方法。简单来说,就是设计一个函数 $ h(x) $ ,把任意结点$ x $映射到 $ [0, M-1] $ 内的整数即可,其中$ M $根据可用内存大小自选。在理想情况下,只需开一个大小为$ M $的数组就能判重。但有时候不同结点的哈希值可能相同,就需要把哈希值相同的状态组织成链表
代码
出自紫书
有几处值得学习的小技巧,比如定义“状态”类型、用两个数组来模拟单向链表、用“引用”简化代码等
eight_nums.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef int State[9]; // 定义“状态”类型
const int MAXSTATE = 1e6;
State st[MAXSTATE], goal; // 状态数组。所有状态都保存在这里
int dist[MAXSTATE]; // 距离数组
const int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
const int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
const int MAX_HASH_SIZE = 1e6 + 3;
int head[MAX_HASH_SIZE], next_[MAXSTATE]; // 模拟单向链表
void init_lookup_table() { // 初始化查找表
memset(head, 0, sizeof(head));
}
int myhash(State &s) { // 哈希函数;
int v = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) v = v * 10 + s[i]; // 把9个数字合成9位数
return v % MAX_HASH_SIZE; // 确保hash函数是不超过hash表的大小的非负整数
}
int try_to_insert(int s) {
int h = myhash(st[s]);
int u = head[h]; // 从表头开始查找链表
while (u) {
if (memcmp(st[u], st[s], sizeof(st[s])) == 0) return 0; // 找到了,插入失败
u = next_[u]; // 顺着链表继续找
}
next_[s] = head[h]; // 插入到链表中
head[h] = s;
return 1;
}
int bfs() {
// BFS,返回目标状态在st数组下标
init_lookup_table(); // 初始化查找表
int front = 1, rear = 2; // 不使用下标0,因为0被看作“不存在”
while (front < rear) {
State &s = st[front]; // 用“引用”简化代码
if (memcmp(goal, s, sizeof(s)) == 0) return front; // 找到目标状态,成功返回
int z;
for (z = 0; z < 9; z++) if (!s[z]) break; // 找“0”的位置
int x = z/3, y = z%3; // 获取行列编号(0~2)
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int newx = x + dx[d];
int newy = y + dy[d];
int newz = newx * 3 + newy;
if (newx >= 0 && newx < 3 && newy >= 0 && newy < 3) { // 如果移动合法
State &t = st[rear];
memcpy(&t, &s, sizeof(s)); // 拓展新结点
t[newz] = s[z];
t[z] = s[newz];
dist[rear] = dist[front] + 1; // 更新新结点的距离值
if (try_to_insert(rear)) rear++; // 如果成功插入查找表,修改队尾指针
}
}
front++; // 拓展完毕后在修改队首指针
}
return 0; // 失败
}
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("eight_nums.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("eight_nums_.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) cin >> st[1][i]; // 起始状态
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) cin >> goal[i]; // 目标状态
int ans = bfs(); // 返回目标状态的下标
if (ans > 0) cout << dist[ans] << endl;
else cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
思考
除了哈希外,还有很多方法,比如编码、A*、STL set(效率低,仅作“跳板”)等,等学到了就来试试(
参考文献
- 刘汝佳《算法竞赛入门经典(第2版)》