AI Translated from Chinese
Problem
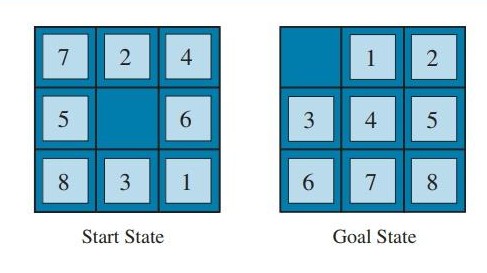
Familiar with Klotski? Or the Number Slide game that came with Win7? The 8-Puzzle problem is derived from this game:
Given 1~8 numbered square tiles arranged in a 3×3 grid, with one cell empty. Each move allows you to slide a tile adjacent to the empty space into the empty cell. Given an initial state and target state (empty space represented by 0), find the minimum number of moves, or output
-1if the target is unreachable.
Analysis
This is also BFS for shortest path. But we need to check for duplicates — avoid visiting the same state multiple times, otherwise it would waste significant time and space.
For this problem, Hash is a feasible and efficient method. Simply put, we design a function h(x) that maps any node x to an integer in the range [0, M-1], where M is chosen based on available memory. In the ideal case, we only need an array of size M to check for duplicates. However, sometimes different nodes may have the same hash value, so we need to organize states with the same hash value into a linked list.
Code
From the “Algorithm Competition Introduction Classic”
There are some worth-learning tips, such as defining a “state” type, using two arrays to simulate a singly-linked list, and using “references” to simplify code.
eight_nums.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef int State[9]; // Define "state" type
const int MAXSTATE = 1e6;
State st[MAXSTATE], goal; // State array. All states are stored here
int dist[MAXSTATE]; // Distance array
const int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
const int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
const int MAX_HASH_SIZE = 1e6 + 3;
int head[MAX_HASH_SIZE], next_[MAXSTATE]; // Simulate singly-linked list
void init_lookup_table() { // Initialize lookup table
memset(head, 0, sizeof(head));
}
int myhash(State &s) { // Hash function
int v = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) v = v * 10 + s[i]; // Combine 9 digits into a 9-digit number
return v % MAX_HASH_SIZE; // Ensure hash function returns non-negative integer within hash table size
}
int try_to_insert(int s) {
int h = myhash(st[s]);
int u = head[h]; // Start searching from the list head
while (u) {
if (memcmp(st[u], st[s], sizeof(st[s])) == 0) return 0; // Found, insertion failed
u = next_[u]; // Continue along the linked list
}
next_[s] = head[h]; // Insert into linked list
head[h] = s;
return 1;
}
int bfs() {
// BFS, returns index of target state in st array
init_lookup_table(); // Initialize lookup table
int front = 1, rear = 2; // Don't use index 0, as 0 means "doesn't exist"
while (front < rear) {
State &s = st[front]; // Use "reference" to simplify code
if (memcmp(goal, s, sizeof(s)) == 0) return front; // Found target state, return success
int z;
for (z = 0; z < 9; z++) if (!s[z]) break; // Find position of "0"
int x = z/3, y = z%3; // Get row and column numbers (0~2)
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int newx = x + dx[d];
int newy = y + dy[d];
int newz = newx * 3 + newy;
if (newx >= 0 && newx < 3 && newy >= 0 && newy < 3) { // If move is valid
State &t = st[rear];
memcpy(&t, &s, sizeof(s)); // Expand new node
t[newz] = s[z];
t[z] = s[newz];
dist[rear] = dist[front] + 1; // Update distance of new node
if (try_to_insert(rear)) rear++; // If successfully inserted into lookup table, update rear pointer
}
}
front++; // After expanding, update front pointer
}
return 0; // Failed
}
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("eight_nums.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("eight_nums_.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) cin >> st[1][i]; // Initial state
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) cin >> goal[i]; // Target state
int ans = bfs(); // Returns index of target state
if (ans > 0) cout << dist[ans] << endl;
else cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
Thoughts
Besides Hash, there are many other methods, such as encoding, A*, STL set (low efficiency, only as a “stepping stone”), etc. I’ll try them when I learn more.
References
- Liu Rujia “Algorithm Competition Introduction Classic (2nd Edition)”